Because the professor advised us to keep an annotated bibliography of every single source we found, even if we only gave each source a glance, I constructed a 20 page document by the end of the quarter, arranged by order of finding the document and comments:
Below is my annotated bibliography, including only the most prominent sources I used this quarter in my writing. This includes sources that were prominent in composing my Historical Conversations Project and Advocacy Project.
Biamonte, Ethan. “The SAT and Admission: Racial Bias and Economic Inequality”. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. 15 November 2013. Web. 25 January 2016.
-Biamonte is an undergraduate student and member of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Class of 2016. The paper proves and evaluates bias against select groups on the SAT, including minority and lower SES students. He does so through graphical analysis and standard deviation functions. Additionally, he points out the unfairness of test-prep coaching as a means of gaining a higher score for more privileged students. The low scores in different social groups shown in this research paper correlate closely to the reduced school attendance cited as a cause of parental involvement, making this paper a convenient comparison.
Cotton, Kathleen and Wikelund, Karen Reed. “Parent Involvement in Education”. School Improvement Research Series. May 1989. Web. 21 January 2016.
-The paper is from the School Improvement Research Series, a product of the Northwest Regional Educational Library, which operates under the Office of Educational Research and Improvement U.S. Department of Education's guidance. Though the source is old, it provides a definition and evaluation of parental involvement. Therefore, my purpose for using the document does not rely on a current change in the course of parental involvement, so the publication date is not a concern. The article also addresses the connections between parent involvement and disadvantaged students.
Davis, Julie Hirschfield. “President Obama Signs Into Law a Rewrite of No Child Left Behind”. New York Times.10 December 2015. Web. 21 January 2016.
-This New York Times article by Julie Davis, a journalist who usually writes about Congress, reports on the recent signing of the new bipartisan measure based on No Child Left Behind. Here, she uses her knowledge of 1965's Elementary and Secondary Education act and makes connections between the old act and the new bill by evaluating the changes that have taken place in between.
"'Helicopter Parents’ Stir up Anxiety, Depression”. Indiana University News Room. 2013. Web. 21 January 2016.
-As a counter argument to the American public schooling system's insufficient parental involvement, the article provides information on parents who go overboard with their involvement in the school system as "helicopter parents". Some parents choose to hover over their students, constantly analyzing their academic progress. This causes students to worry about what their parents think, which can ultimately lead to anxiety and depression.
Fabian, Jordan. “Obama signs education reform bill.” The Hill. Capitol Hill Publishing Corp. 10 December 2015. Web. 29 January 2016.
-Fabian is a journalist with a focus in politics, specifically in campaigns, congress, and immigration. His paper provides a quality review of the new education reform bill signed by Obama, the Every Student Succeeds Act. As a political analyst, Fabian admires the bill's transfer from large-scale to small-scale government, making the small-scale solutions posed for parental involvement seem more feasible in America's new condition.
George Mason University Student Organization. “Purpose of IECA.” International Education and Cultural Awareness Organization. n.d. Web. 15 February 2016.
-The International Education and Cultural Awareness Organization, or IECA, was developed at George Mason University, and fundraisers in order to work in tandem with other nonprofits. Some of their events include screening documentaries, fundraisers, and visiting local high schools to help students with college applications. For this reason, their mission statement and goals line up with those of a one-stop community center, which is proposed in the Advocacy project.
Gutierrez, Elli. “Public Schools vs. Charter Schools.” Blogspot. 13 October 2014. Web. 16 February 2016.
-Gutierrez explains some of the benefits and costs that come with implementing charter schools in the American school system. She mentions their proliferation in more recent years and even provides a graphic bubble map distinguishing the elements of charter schools and traditional public schools. One key element she mentions is that, even if charter schools are sometimes less transparent, they are given certain expectations, making them accountable for the education of their students.
jeffdowd. “The Problem with ‘Failing Schools’”. The Society Pages. 10 March 2011. Web. 10 February 2016.
-The article in this source is written and submitted on “The Sociology Lens”, which is a small subsection of the website “The Society Pages”. The website provides information specifically to scholars and graduate students via journal entries in order to discuss pressing issues in sociology. The article outlines the fact that new studies are revealing that parents are the ones to blame for their children’s behavioral and educational problems, but that this approach is overly simplistic. In the case of this advocacy project, the political cartoon is a great way to debate the true causation of a lack of parental involvement. Did the pillar get knocked down by itself? Did another pillar contribute to the fall of the “parental pillar”? The political cartoon provides a great multimodal element along with the debate in the online article.
Kirp, David L. “How to Fix the Country’s Failing Schools. And How Not To.” New York Times. 9 January 2016. Web. 25 February 2016.
-As a professor of public policy at the University of California, Berkeley and an opinion writer for the New York Times, Kirp keeps his focus on America's educational issues by analyzing educational policy. The article provides an analysis of Union City, and why hiring bilingual staff in a system with a high ESL population raised proficiency in reading. The bilingual staff created an opportunity for students to learn in comfort while stretching their boundaries by experiencing more of the English language.
Lee, Phillip. “The Curious Life of In Loco Parentis at American Universities”. Higher Education in Review. 2011. Web. 21 January 2016.
-Lee’s article mainly discusses the aspect of “in loco parentis”, which frames the original motivation behind a lack of parental engagement with their child. The author is an instructor in education from Harvard University and has written several other articles on issues regarding student ethnicity, activism, and diversity. His reputation and articles make him a credible source of information regarding students, demographics in universities, and even the relationship between the two. In loco parentis is a great tool to begin to introduce the concept of traditional public schools and universities taking on the responsibilities of parents, thus exercising accountability. Linked to accountability are many reform ideas and debates about holding parents accountable in a measureable way, which the advocacy project will discuss.
Lynch, Matthew. “6 Ways Teachers Can Foster Cultural Awareness in the Classroom.” Education Week. 30 November 2014. Web. 15 February 2016.
-Matthew Lynch is author of the book The Call to Teach and the editor of the edvocate, an online archive of news with a focus on student teaching and curriculum. In his Huffington Post article, Lynch advocates for a "culturally responsive curriculum", or a way of teaching that fosters the needs of all students. When teachers adopt this policy, they are making a pledge to ensure that all students feel included in their classroom environment.
McDermott, Peter and Rothenberg, Julia. “Why Urban Parents Resist Involvement in their Children’s Elementary Education”. The Qualitative Report, Volume 5. October 2000. Web. 21 January 2016.
-Two professors of The Sage Colleges, one focused on preparing teachers for urban education and another with a focus in teaching inclusion to graduate students, evaluate the reasoning behind insufficient parent involvement. Their analysis of the American education system reveals that public education has long been geared more towards middle class white students, or the original majority population of the nation. Now that the population is more diverse, the old teaching methods and curriculum are not as effective, setting many students, especially lower income and urban students, at a disadvantage.
NEA Education Policy and Practice Department. “Parent, Family, Community Involvement in Education”. Washington D.C.: National Education Association. 2008. Print. 29 February 2016.
-The National Education Association (NEA) aims to create a fair educational experience for students nationwide. In thier policy brief, research reveals relationships between parents, families, communities, and staff of schools. Introducing the brief with the quote "it takes a village to raise a child" helps the writers frame their argument, and they later support this statement with clear and consistent research on the benefits of everyone in the community working together to ensure equality in the education system.
Ohio Department Of Education. “21st Century Community Learning Centers (CCLC).” 16 February 2016. Web. 21 January 2016.
-Introducing a new program, the Ohio Department of Education (ODE) has opened up a program for schools with students who are low-performing and of a lower socioeconomic status. The program was introduced beginning in the 2015-2016 school year, making this source current. Organizations receive grants from the ODE if they provide a good claim and can promote the wellbeing of the disadvantaged students.
“Our History”. americaspromise.org. America’s Promise Alliance, n.d. Web. 27 January 2016.
-America’s Promise Alliance is a foundation that collaborates with both government and non-government organizations in order to encourage children of all socioeconomic standings to gain an education. The foundation began in 1997 with a declaration aimed at making “children and youth a top national priority” and was signed by various presidents including Ford, Carter, Reagan, Bush, Clinton, and more recently president Obama(APA).
“Parental Involvement: Title I, Part A”. No Child Left Behind. 23 April 2004.
-Title I is a key component of multiple reforms, including No Child Left Behind and the Every Student Succeeds Act. This part of the bill declares that students of lower income need supplemental educational assistance in their schooling. Title I aims to collaborate with parents to create a unique written policy for each school based on their students and their average income.
Ravitch, Diane. The Death and Life of the Great American School System. New York: Basic Books, 2011. Print.
-Sharing her rich knowledge of the history of school reforms, Ravitch crafts a text that reflects upon various moments in history and concepts in the school reform system. She is a professor at New York University and has worked with Secretary of Education Lamar Alexander and Presidents Bill Clinton and George Bush. Because of her experiences and knowledge, GASS provides a credible account of the history of school reform that can be used anywhere from a simple quoting to a complex analysis referencing Ravitch as an expert. The book speaks of several aspects that organizations, philanthropists, and public officials focus on when changing schools, including (but not limited to) corporate reform, standardized testing, accountability, Common Core, and No Child Left Behind. Practically any aspect of the school system can be covered by this novel; if not directly, topics in this book can be linked to other specific topics talked about by other scholars.
*This was our class text, a crucial element in learning about the American education system. Ravitch's knowledge of the way the education system works made her a credible source for every topic I needed information on.
Reid, Ken. Truancy: Short and Long-term Solutions. Florence: Routledge, 2004. Print.
-This short novel discusses the occurrences in which students choose to be truant to school. Ken Reid is a secondary teacher at Berkshire and at Oxfordshire and even took teaching positions in Cardiff and Leicester for higher education purposes. His work revolves around issues regarding school attendance (and a lack of school attendance, or truancy) as well as constantly utilizing behavioral studies of students for his writing. Because of his rich knowledge in the field of student attendance rates, “Truancy: Short and Long-term Solutions” provides not only an account of the kids who are truant and behaving poorly but also the parents who nurture these students. This includes laissez-faire parents, a term he uses for the parents who allow their kids all of the freedoms they desire, and even anti-education parents, or those who advocate against the ongoings in the realm of education.
Shapiro, Eliza. “De Blasio to announce $186 million in new education policies.” Politico New York. 16 September 2016. Web. 1 March 2016.
-In New York City, Mayor Bill de Blasio shows great interest in the harmony between charter schools and traditional public schools. Shapiro, a reporter for Politico focused on city policy and education, elucidates de Blasio's desire for student equality, a principal also reflected in No Child Left Behind. Overall, the article show just how much education reform costs, even on a small-scale, one district project.
Sheehy, Kelsey. “High School Dropouts Blame lack of Parental Support, Teen Pregnancy.” U.S. News and World Report: Education.14 November 2012. Web. 21 January 2016.
-A report from U.S. News and World Report states that high dropout rates in public schools are caused by unengaged parents and teenage pregnancy, which is also caused by insufficient parental involvement. Sheehy communicates that, without involved parents, a student is unable to learn as efficiently as those privileged with extra assistance.
“Summary of the Every Student Succeeds Act, Legislation Reauthorizing the Elementary and Secondary Education Act.” National Conference of State Legislatures. 2015. Web 21 January 2016.
-The National Conference of State Legislatures is an bipartisan NGO dedicated to making state power a priority over federal power. This nonprofit collaborates with Congress in order to balance power and efficiently allocate governmental funds. The summary also contains information about the legislative history of the act and even the authorization of grants in Title I.
Taylor, Kate. “A Push to Involve Parents at Struggling Schools.” New York Times. Print. 21 January 2016.
-Kate Taylor is a reporter for the New York Times and focuses on schools in New York City. Taylor’s article reports on the lack of parental involvement in New York City’s schools and Mayor Bill de Blasio’s attempts at raising up low performing schools. Unlike the Bloomberg administration’s targeting of weak staff and schools, de Blasio aims to create better schools through one-stop community centers. These centers would help parents become more involved in their children’s education. Additionally, the administration is making efforts to make parents of children in the school system aware that they can be involved in the school system.
Thompson, Carolyn. “Charter Schools Benefit Minorities, Poor Families Most, Study Shows.” The Huffington Post. Huffpost Black Voices. 25 June 2013. Web. 22 February 2016.
-Thompson of The Huffington Post provides an analysis of charter schools throughout the years, comparing findings from 2009 and 2013. She discovers that, although charter schools were originally performing below average compared to traditional public schools, charter schools are constantly improving beyond their old scores and even beyond the public schools they were originally performing under. Thompson addresses that the charter schools provide a good opportunity for lower performing students and will promote equality when regulated. Studies in the article show that low performing students get more out of each day of learning in a charter school than in a standard school.
“Title I- Improving The Academic Achievement Of The Disadvantaged.” U.S. Department of Education. 15 September 2004. Web. 21 January 2016.
-An account of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, which was originally passed during Lyndon B. Johnson's "War on Poverty." For this reason, the act aimed at targeting underprivileged students who could not gain a high-quality education. For this reason, the act made schools figure out how they were to allocate Title I funds to families, as the act did not directly enforce how schools were to use the money.
Utah Charter Schools Act. Chapter 150, 2015 General Session. Print. 25 February 2016.
-The act reviews the purpose of Charter schools and the way that they are run. This document classifies charter schools as prominent opportunities for both students and parents to become involved in the American education system. Parents can do so by becoming involved in both their student's progress and in parent teacher organizations.
United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. English Language Learners. 2012-13. Web. 6 March 2016.
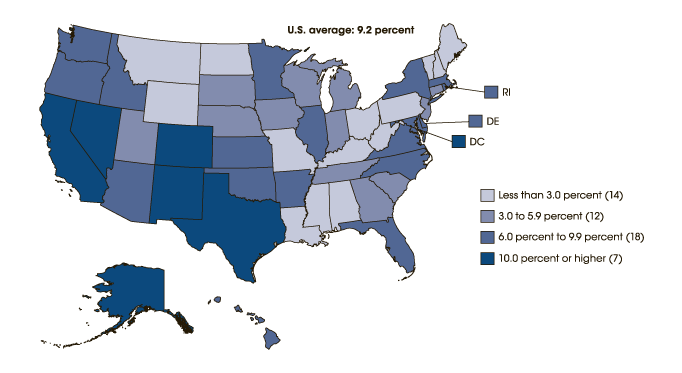
-The article provides a great graphic showing the percentage of English language learners in the public school system by state. The stately average is around 9.2 percent, but some of the large states like California and Texas contain over 10 percent of English language learners in the public school system. As indicated by these high numbers, America's school system must do something to make sure that ESL students are on par with the majority of the public schooling system.
 icons at the top right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top right corner of the subsection.